Intel has added new CPUs to the Cascade Lake family and here are a few things you should know about these new Refresh CPUs before buying your next blade server.
Known as the Intel “Cascade Lake Refresh”, these newly released CPUs are part of the existing 2nd Generation Intel Xeon SP CPU family. In fact, you can easily identify these new CPUs with the “R” at the end of the Intel model number. So why is Intel doing another refresh? After all, they just refreshed the 1st Generation Xeon SP last April. According to one Intel source, they introduced these new CPUs to help deliver “platinum level performance at gold prices.” As you’ll see in the chart below, Intel delivers on this goal – but I’m getting ahead of myself. Let me give you some of the things you need to know about the 2nd Generation Intel Xeon SP Refresh CPUs.
Existing Intel CPUs Aren’t Going Away
In the past, we’ve gotten used to Intel phasing out CPUs once new ones are introduced. That is not the case with the 2nd Generation Intel Xeon SP Refresh CPUs. They aren’t replacing any CPUs but instead are NEW additions. If you don’t like the “-R” CPUs, don’t worry – you can continue buying what you’ve been buying.
You Won’t Get Large Memory With Them
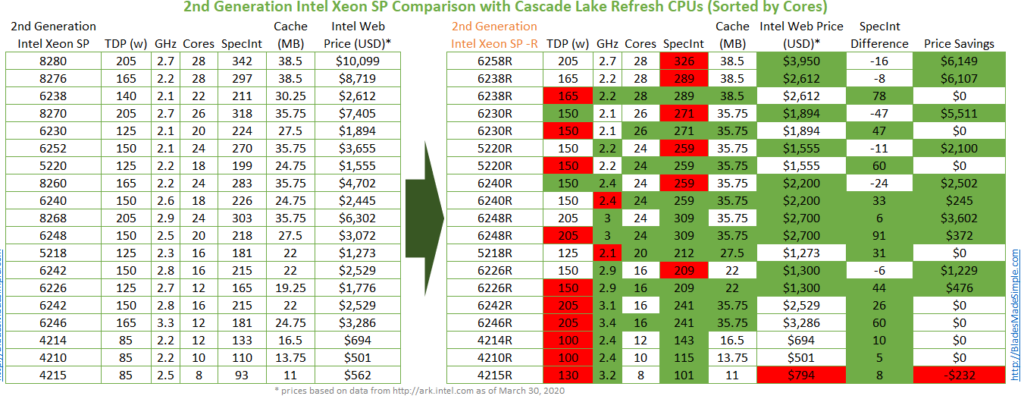
As you look at the chart below, you’ll notice there are not any CPUs with the “-L” suffix therefore the maximum memory you are able to run with these offerings is 1TB per CPU (same as the existing 2nd Generation Intel Xeon SP CPUs.) This is very important to realize, as if you invest in these CPUs and decide you want to load up your servers with memory, you risk going above that 1TB of RAM / CPU hard limit that Intel set which means your server won’t boot. I can’t say whether or not Intel will ever add larger memory support on these “-R” CPUs so for now, if you need large memory support, these CPU’s aren’t for you.
No Support on 4 Socket Servers
I’ve also confirmed with Intel that these new “-R” CPUs are only supported with 2 CPU server designs. They will not be supported on 4 socket servers. (Don’t shoot the messenger.)
Most Offer Higher Frequencies, Cores, Cache and Sometimes TDP
If you didn’t figure it out, the chart below is a comparison between the 2nd Generation Intel Xeon SP CPUs and the “Cascade Lake Refresh” CPUs. The green blocks show where the “-R” CPUs have an advantage versus the CPU on the left. In most of the comparisons, the “-R” CPUs offer higher frequencies, more cores, higher cache at a lower price. The trade-offs, however could be a lower performance (SpecInt) or higher TDP (Thermal Design Power).
To assist you with your decisions, I’ve created a PDF with 5 variations of the chart below: sorted by cores, GHz, SpecInt, Savings and TDP. Download it here: 2nd Generation Intel Xeon SP Comparison with Cascade Lake Refresh CPUs (PDF – 800kb)
Learn more about Intel’s 2nd Generation Xeon SP CPUs including the Refresh CPUs at https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/design/products-and-solutions/processors-and-chipsets/cascade-lake/2nd-gen-intel-xeon-scalable-processors.html
 Kevin Houston is the founder and Editor-in-Chief of BladesMadeSimple.com. He has over 20 years of experience in the x86 server marketplace. Since 1997 Kevin has worked at several resellers in the Atlanta area, and has a vast array of competitive x86 server knowledge and certifications as well as an in-depth understanding of VMware and Citrix virtualization. Kevin has worked at Dell EMC since August 2011 is a Principal Engineer and Chief Technical Server Architect supporting the Central Enterprise Region at Dell EMC. He is also a CTO Ambassador in the Office of the CTO at Dell Technologies.
Kevin Houston is the founder and Editor-in-Chief of BladesMadeSimple.com. He has over 20 years of experience in the x86 server marketplace. Since 1997 Kevin has worked at several resellers in the Atlanta area, and has a vast array of competitive x86 server knowledge and certifications as well as an in-depth understanding of VMware and Citrix virtualization. Kevin has worked at Dell EMC since August 2011 is a Principal Engineer and Chief Technical Server Architect supporting the Central Enterprise Region at Dell EMC. He is also a CTO Ambassador in the Office of the CTO at Dell Technologies.
Disclaimer: The views presented in this blog are personal views and may or may not reflect any of the contributors’ employer’s positions. Furthermore, the content is not reviewed, approved or published by any employer. No compensation has been provided for any part of this blog.
Pingback: What You Need To Know About The Intel Cascade Lake Refresh – Real World UCS